As Ethereum continues to grow, layer 2 solutions have emerged to tackle the challenges of scalability. These solutions have made significant strides in overcoming technological barriers, resulting in an impressive increase in the availability of layer 2 platforms. Initially restricted to state channels, plasma chains, and application-specific rollups, the landscape now features general-purpose rollups such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync, with industry giants like Coinbase entering the arena with their Base layer 2 and others expected to follow suit.
The appeal of layer 2 solutions lies in their lower transaction fees, faster speeds, thriving dapp ecosystems, and potential airdrops. This has led to a surge in users, pushing layer 2s to process five times the number of transactions compared to the Ethereum mainnet in less than a year. With the market for layer 2 solutions becoming increasingly competitive, this article aims to provide an overview of the key players, as well as an in-depth analysis of the features that could set one layer 2 solution apart from the rest.
Why are Layer 2 Solutions Necessary?
Balancing Scalability, Security, and Decentralization
One challenge in blockchain design is finding a balance between scalability, security, and decentralization. High-throughput blockchains like Solana require significant hardware capabilities to handle processing demands. Consequently, fewer parties can run nodes, leading to potential power concentration and increased vulnerability to manipulation and majority attacks.
Ethereum, on the other hand, has relatively low hardware requirements for running a node, which encourages decentralization and strengthens security. This design choice, however, leads to a compromise on scalability - Ethereum can process a maximum of around 30 transactions per second (tps), whereas Solana can theoretically process 65,000 tps. As the number of use cases and users expands, scalability becomes crucial in achieving success for these networks.
Early Indications of Layer 2's Necessity
As blockchain technology evolved and use cases extended beyond peer-to-peer transactions, Ethereum's scalability limitations became more pronounced. When CryptoKitties, a popular Ethereum-based game, went viral in 2017, transaction fees and wait times surged dramatically. This event underscored the need for blockchain networks to process transactions rapidly and offer lower fees to support more users and complex decentralized applications.
Following the 2021 bull market, Ethereum transaction fees peaked at over $200, further emphasizing the urgency for improved scalability. Layer 2 solutions were introduced to address such challenges without compromising security and decentralization.
Layer 2 solutions not only enhance transaction efficiency, speed, and scalability but also serve as a transformative component in blockchain technology's future. Innovations behind these solutions, such as State Channels, Plasma, and Rollups, are pivotal in driving the advancement of blockchain networks to support a diverse array of use cases.
Understanding Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions are designed to enhance an existing Layer 1 blockchain, such as Ethereum, by improving its performance and capabilities. These solutions increase transaction throughput and speed by processing transactions off-chain, reducing the computational workload on the main chain and allowing it to scale.
These scaling improvements result in significantly faster and more affordable transaction fees, making blockchain technology accessible to a broader user base, who might otherwise be deterred by prohibitive costs. For example, using Optimism for sending ETH between addresses could cost users as low as $0.09, compared to $1.24 on the Ethereum Network.
Clarifying the Difference: Why Polygon Proof-of-Stake is Not Considered Layer 2
Polygon's Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain is often linked to Layer 2 solutions due to its high throughput and efficient bridging capabilities with Ethereum. Despite these similarities, it is not a Layer 2 solution due to differences in its security model.
Unlike Layer 2 solutions that derive security directly from Ethereum's consensus protocol, the Polygon PoS chain operates using its own consensus mechanism and set of validators. This structure classifies it as a sidechain – a separate blockchain that runs parallel to the primary chain, with distinct security assumptions and rules – rather than a Layer 2 solution.
Today's Rollup-Centric Layer 2 Landscape
How Rollups Enhance Ethereum's Scalability
Rollups are an increasingly popular Layer 2 scaling solution that address Ethereum's scalability challenges. They enable Ethereum decentralized apps (dApps) to work with minimal or no code changes, as opposed to other Layer 2 solutions like payment channels.
Rollups enhance Ethereum's scaling capabilities by moving computation off-chain, which alleviates the burden on the main chain. Transactions are processed off-chain, with data then being compressed and added to Ethereum in batches. Each batch contains essential transaction data and the updated rollup state.
The critical aspect of rollups is proving the validity of the new state to Ethereum. This can be achieved through either fraud proofs or validity proofs, depending on whether the rollup in question is optimistic or zero-knowledge based. The gas fees for submitting the required data for multiple off-chain transactions and verifying either type of proof are considerably lower than performing the original computation directly on the Ethereum network. As a result, rollups greatly increase transaction throughput and reduce costs.
By maintaining the rollup state within the Ethereum network, rollups ensure strong security guarantees as users always possess the necessary information to verify transactions. Overall, rollups provide a promising solution to Ethereum's scalability issues while maintaining robust security levels.
The Leading Layer 2 Solutions
Notable Layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync, and Base dominate the rollup-focused market. There are a few other Layer 2s like Mantle Network and Immutable X that we will not cover for the sake of the article's length. Key players in the industry differ based on the total value locked within their respective solutions. By accelerating transaction speed and improving scalability, these L2 technologies enable secure and efficient trading on platforms like Ethereum and decentralized exchanges. Top-ranking rollups feature various use cases, including proof-of-stake systems, payments, and yield farming.
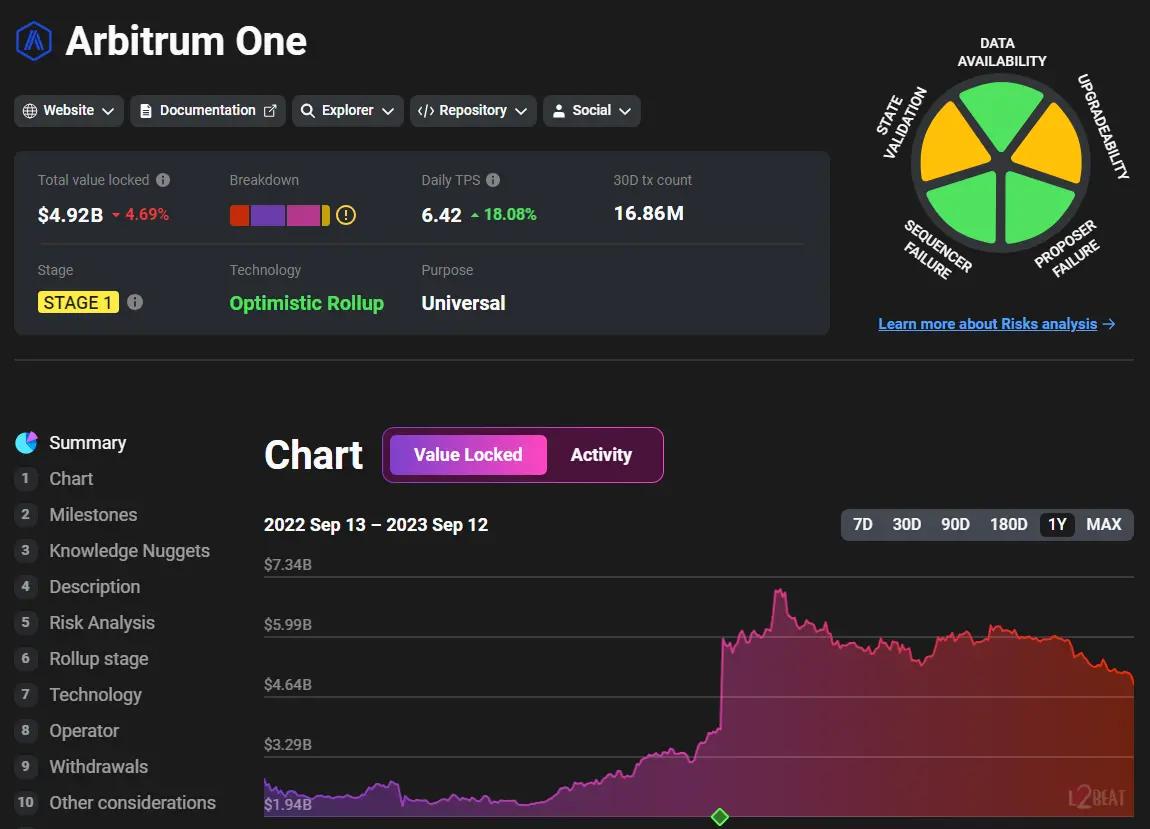
Arbitrum: The Most Mature Rollup
Arbitrum Governance
Arbitrum uses an on-chain governance model, managed by the Arbitrum decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). ARB token holders have voting power proportional to their token holdings, allowing them to participate in governance proposals.
In addition to the DAO, a Security Council made up of 12 respected community representatives is responsible for maintaining chain security during emergencies such as security vulnerabilities. The Arbitrum DAO oversees the Security Council and holds elections for council members twice a year.
The Arbitrum Token: ARB
The ARB token serves as a governance token for the Arbitrum ecosystem, with an initial maximum supply of 10,000,000,000 tokens. The distribution of ARB tokens is as follows:
- 11.6% awarded to early Arbitrum users via Airdrop
- 1.1% awarded to DAOs in the Arbitrum ecosystem via Airdrop
- 42.8% allocated to the Arbitrum DAO Treasury, with governance determining the usage of funds
- 26.9% allocated to Core Contributors, including Offchain Labs team, treasury, and advisors
- 17.5% allocated to Offchain Labs investors
Arbitrum became popular as the first optimistic rollup capable of supporting Ethereum dApps with minimal coding changes. It is now the leading layer 2 by total value locked, hosting a thriving DeFi ecosystem. Governed by the Arbitrum DAO, with the Arbitrum Foundation as its steward, the ecosystem continues to grow and evolve under the guiding hand of Offchain Labs, a blockchain development company responsible for network upgrades.
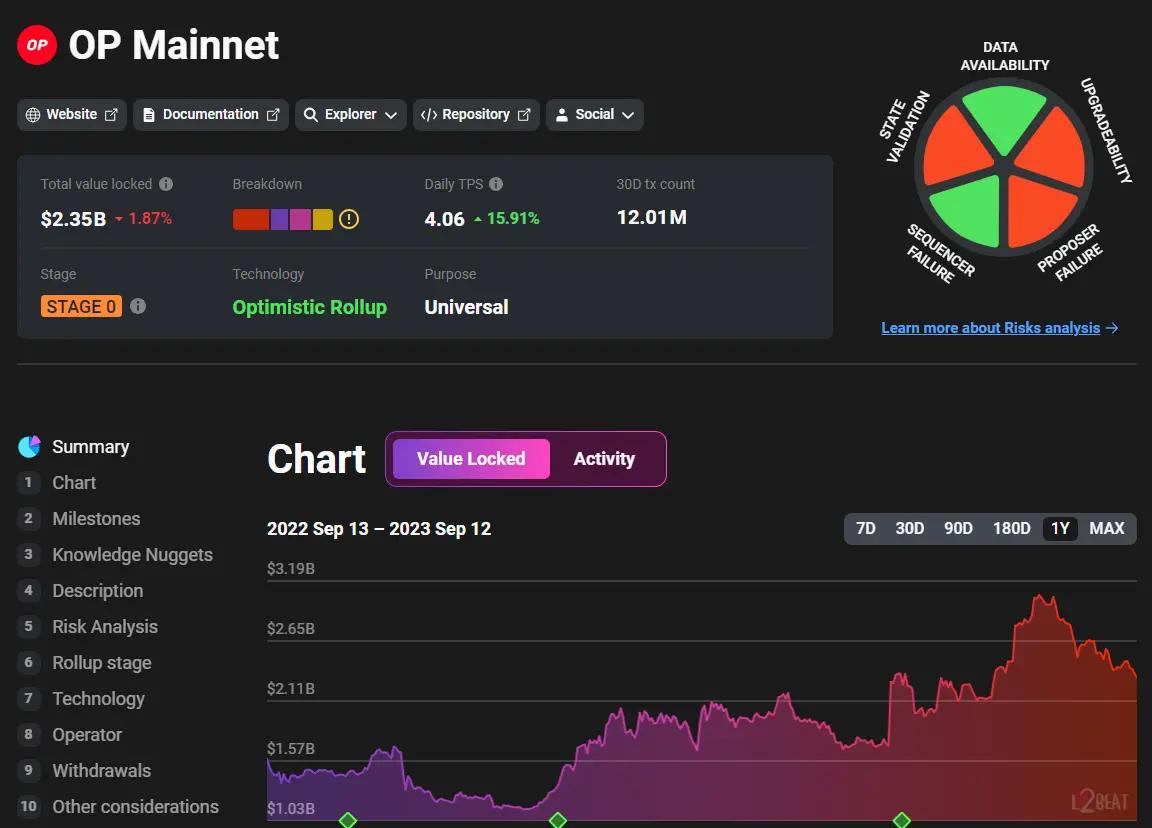
Optimism: The Superchain
Enabling Software: The OP Stack
Optimism depends on its revolutionary open-source software package called the "OP Stack." This software allows for the development of compatible Layer 2 and Layer 3 solutions, referred to as "op-chains." These op-chains can communicate through a shared message-passing format, ultimately creating what is known as the "Superchain." The Superchain aims to offer the scalability of parallel chains and the composability of a single blockchain.
The Optimism Collective: Innovative Governance
The Optimism Collective, an advanced governance system, oversees the network's progress. It is divided into two main sections: the Token House and the Citizens’ House.
Token House
Holders of the OP token have voting rights in the Token House, permitting them to weigh in on matters like protocol upgrades and the allocation of the Governance Fund, similar to a DAO treasury.
Citizens’ House
The Citizens’ House directs the distribution process for retroactive public goods funding. Membership, or "citizenship," is granted through non-transferable NFTs soulbound to their holders. The number of citizens will grow as the Optimism community expands.
Promoting Network Effects: Retroactive Public Goods Funding
Retroactive public goods funding rewards efforts that have already benefited the Optimism ecosystem. This funding method recognizes valuable contributions that could go unrewarded, stimulating network growth. Funding is derived from the initial OP token supply and network transaction fees from Optimism and other op-chains.
The OP Token: Central to Incentives and Governance
The OP token is crucial to the Optimism Collective's vision, acting as the governance token for the Token House and the backbone of the incentives system. The Optimism Collective established a dynamic, governance-driven system of incentives for projects and users in the Optimism ecosystem, centered around the OP token.
Base: The Chain To Onboard Billions of Users

A New Participant in the Optimism Superchain
Launched on August 9th, 2023, Base is the latest optimistic rollup by Coinbase aimed at increasing economic freedom worldwide by providing easy access to the on-chain economy. By joining the Optimism Superchain, Base benefits from a robust, interoperable, and scalable architecture. Furthermore, Coinbase will contribute a percentage of the transaction fees earned through Base to the Optimism Collective, supporting both the Superchain and the broader crypto economy.
Potential Leading Platform for Tokenized Real-World Assets
With every Coinbase user having passed KYC/AML checks, Base has a unique advantage in the layer 2 landscape. Its 110 million verified users experience less friction when trading assets, like securities, that require KYC/AML checks. This positions Base as an ideal platform for deploying real-world blockchain assets.
No Native Base Token
Importantly, Coinbase has explicitly stated that there will not be a native token for Base, warning users to be cautious of scams attempting to impersonate the platform's potential token.
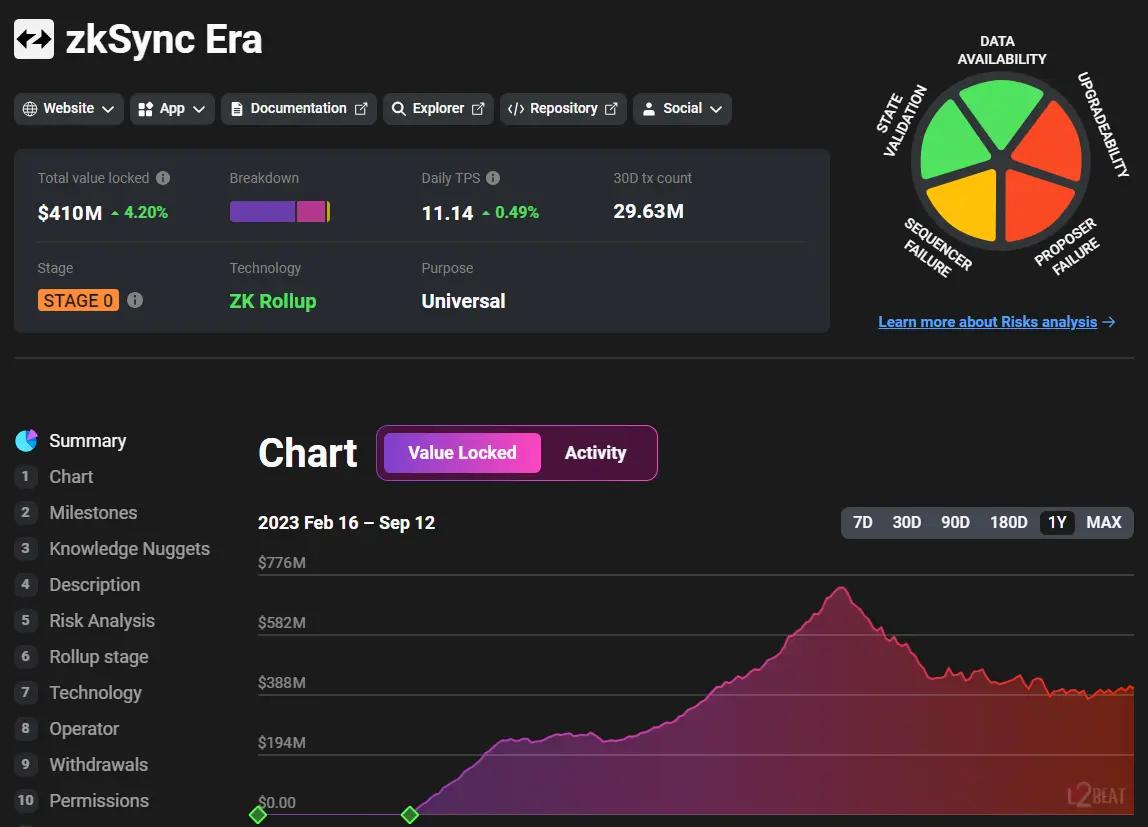
ZkSync Era: The Dark Horse
Launch of zkSync Token: The Wait Continues
ZkSync Era, known for being the first publicly accessible EVM-compatible zk rollup (zkEVM), was launched on March 24, 2023. It has gained attention as the leading solution in Ethereum scaling due to its high scalability, compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVM) and trustless nature. Currently, zkSync Era ranks third in Layer 2s by total volume locked and often achieves first place in transaction activity. This achievement highlights its advanced technology and dominance among other zk rollups, but it's essential to consider that metrics might be inflated due to the potential token airdrop.
The zkSync token has been mentioned in its documentation, but there has been no clear date for its launch. The team has stated that the token would be released when the time is right. Decentralizing the rollup is one of their main objectives, and the token will play a vital role in achieving that goal. However, as the network is in its early stages, maintaining control over upgrades and sequencers is considered more beneficial for users in case any bugs or attacks arise.
As the next step towards decentralization, zkSync Era plans to transition to a community-elected security council model. At that stage, introducing the token will become more meaningful. Until then, users should remain aware of impersonators and scammers who might take advantage of the zkSync token's anticipation.
Comparing Layer 2 Solutions
Technical Components of Optimistic Rollups and Zk Rollups
Optimistic rollups rely on fraud proofs to validate new rollup states. This method allows any validator to contest the state data if it's perceived as invalid. For this process to work, the optimistic rollup must submit adequate transaction data to the underlying blockchain, ultimately enabling challenges to the state. A seven-day window is available for filing fraud proofs, ensuring ample time for disputes.
Zk rollups, on the other hand, utilize validity proofs to confirm the new rollup state's accuracy. These cryptographic proofs (ZK-STARK, or Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge) are used within zkSync to validate data without exposing it. While requiring higher computational costs than fraud proofs, validity proofs offer crucial advantages.
Unlike optimistic rollups, zk rollups do not rely on third parties or economic games for validation. Their trustless nature is derived from mathematics, making zk rollups entirely trustworthy. As validity proofs can be rapidly verified, zk rollups enable faster transaction finalization compared to the seven-day dispute resolution period necessary for optimistic rollups. This means that bridging back to Ethereum is significantly quicker with zk rollups.
Lastly, some zk rollup designs, such as zkSync, only necessitate state root change uploading to the main chain due to their trustless nature. Conversely, optimistic rollups require both transaction data and state root change submissions to the main chain for state challenges to be possible.
Shard Chains: The Impact of Increased Data Availability on Rollups
Shard chains, specifically in the initial form of EIP-4844 (proto-danksharding), promise to make data transfer on the Ethereum network more cost-effective. While there is no definite rollout date, it could potentially occur by late 2023. Affordable and accessible data will benefit both optimistic and zk rollups, leading to significantly reduced transaction expenses.
It should be noted that zk rollups require more resources to verify zk proofs, and as a result, they allocate a smaller portion of gas for data uploading than optimistic rollups. Consequently, the introduction of shard chains will have a more substantial effect on optimistic rollups.
The Current Stage of Leading Rollups
The development stage of rollups is crucial as it can impact their security. Arbitrum has attained a more advanced level of development, being a "stage 1" rollup with necessary features. Comparatively, ZkSync, Base and Optimism are still in "stage 0," meaning certain features are yet to be implemented, thus increasing risks.
For Optimism and Base rollups, understanding that their fraud proof mechanisms are in development is vital. This ongoing work presents significant risks that need further examination and comprehension. Remember, when evaluating rollups, consider the development stage and its effect on the overall security and performance of the blockchain.
Condensing Everything: Who Will Win?
At present, Arbitrum appears to be leading the Layer 2 race, with a dominant position in DeFi and strong rollup security features, as highlighted in Beyond the Giants: A Deep Dive into the Emerging L2 Ecosystem. Thanks to Offchain Labs' diligent work, forthcoming proto-danksharding improvements will further reduce transaction costs for Arbitrum.
In the short term, Arbitrum faces challenges from optimistic rollups like Optimism and Base. Groundbreaking retroactive funding and grants could provide these superchains with a boost, potentially resulting in surging popularity. Coinbase's potential integration of Base is worth monitoring, as it may significantly increase on-chain adoption.
ZkSync, a zk rollup, poses a long-term threat. With a focus on Ethereum scaling efficiency, zk rollups' costs will remain higher than optimistic rollups for the time being. However, as zk technology matures, it's expected that zk rollups will become the preferred option for scaling Ethereum across various applications.
Down the line, non-EVM compatible zk rollups providing specialized environments for increased efficiency could rise to prominence. Starkware, a leader in the field, is currently working on substantial upgrades to their technology stack. In this race to scale Ethereum, it remains to be seen which of these contenders will ultimately prevail in securing widespread adoption and enhancing the user experience for DeFi protocols, dApps, NFTs, and the broader crypto ecosystem.











